The 2025 December, or winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere, will occur on 21 December at 15:03 UTC.
But what does the December solstice mean, and what does it have to do with Earth's orbit around the Sun?
We asked Shyam Balaji, researcher in astroparticle physics and cosmology at King’s College London, to explain.
What is the science behind the December solstice?
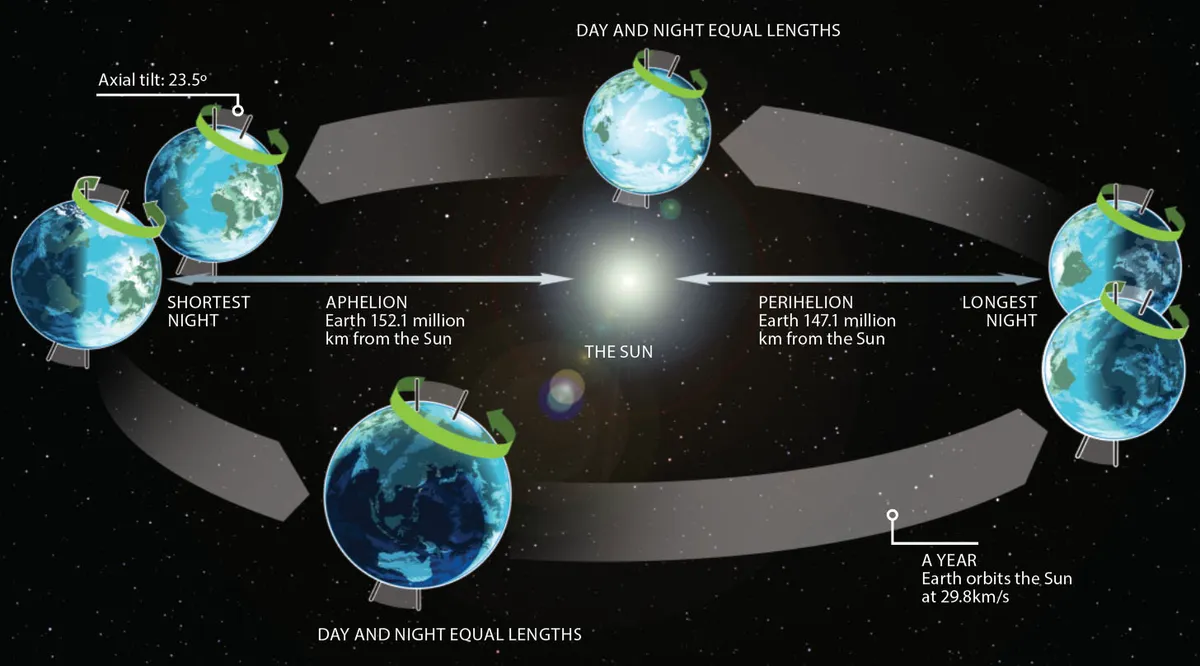
It occurs because the Earth is tilted on its axis by about 23.5 degrees relative to its orbit around the Sun.
This tilt causes different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year.
During the December solstice, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted the farthest away from the Sun, resulting in the shortest day and longest night of the year for that hemisphere.
What does the solstice mean in terms of daylight hours?
The December solstice marks the shortest day and longest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
This means that the amount of daylight is at its minimum, and the night is at its longest. Conversely, in the Southern Hemisphere, it is the longest day and shortest night of the year.

How long is the shortest day of the year?
The length of the shortest day varies depending on your location.
For example, in London, UK, the shortest day lasts about 7 hours, 49 minutes, and 42 seconds.
The exact duration will differ based on how far north or south you are from the equator.
What does the word ‘solstice’ mean?
The word 'solstice' comes from the Latin words 'sol' – sun – and 'sistere' – to stand still.
It refers to the point where the Sun's apparent movement north or south pauses before reversing direction.
After the December solstice, the days start to get longer in the Northern Hemisphere.

