The centre of the Sun crossed the celestial equator at 09:01 UT on 20 March 2025, marking the Northern Hemisphere’s vernal or spring equinox. For those in the Southern Hemisphere, the instant marked their autumn equinox.
And in 2025 the summer solstice occurs on 21 June at 03.42 BST (02.42 UTC).
But what do solstices and and equinoxes actually mean, and why do we mark them on our calendars?
Read on to find out.
Solstices and equinoxes in 2025
- Spring equinox 2025 occurs on 20 March at 09:01 UTC
- Summer solstice 2025 occurs on 21 June at 03:42 BST
- Autumn equinox 2025 occurs on 22 September at 19.20 BST
- Winter solstice 2025 occurs on 21 December at 15.03 UTC
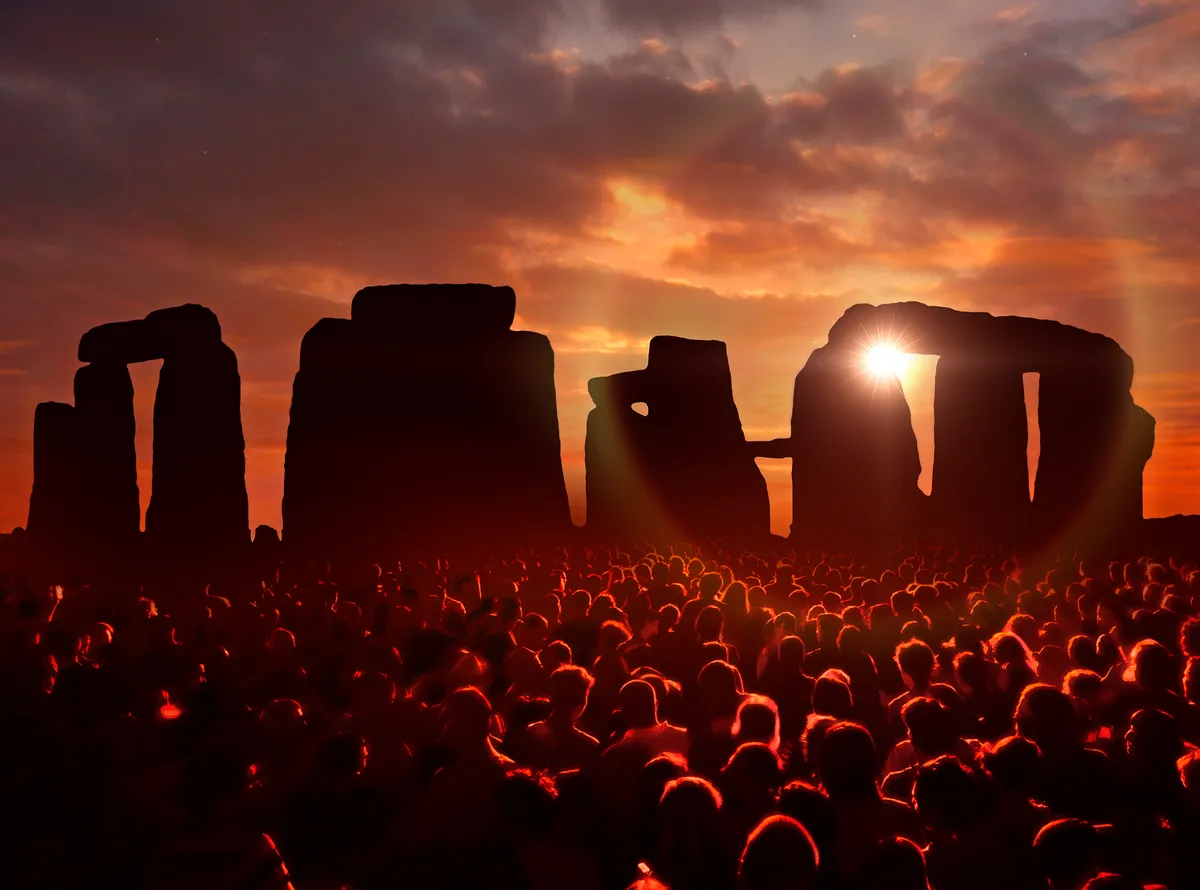

For thousands of years, our ancient ancestors tracked the path of the Sun across the sky.
Watching it rise and set at different positions throughout the year and constructing monuments such as the prehistoric stone circle Stonehenge in Wiltshire to keep track of its movement.
June is a key month in the Sun’s path and also at Stonehenge, where thousands visit to mark the summer solstice – the longest day and shortest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
The word ‘solstice’ comes to us from Latin, ‘sol’ meaning Sun and ‘sistere’ to stand still.
But why does the Sun appear to stand still? And what does it signify in the astronomical calendar?
Join me on a short journey as we follow Earth’s orbit of the Sun and learn why we experience seasons and variations in sunlight throughout the year.
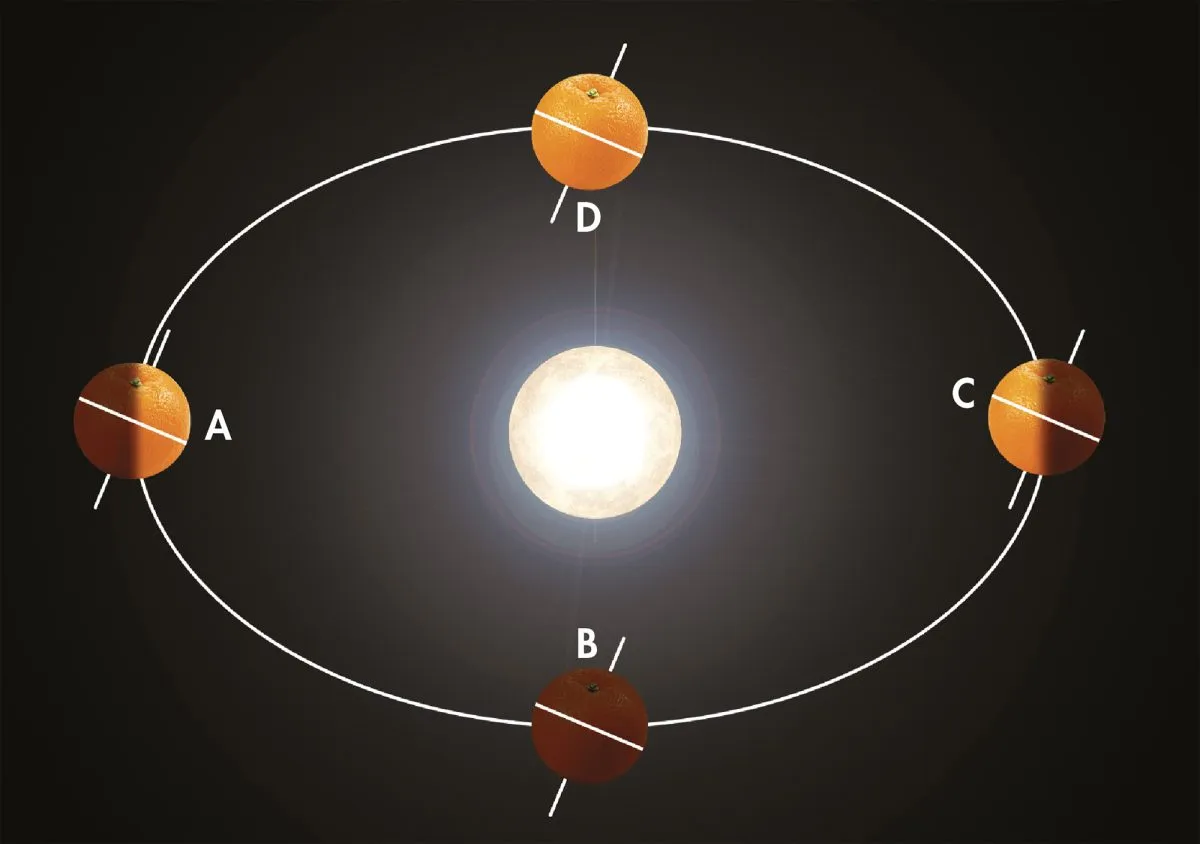
Solstices, equinoxes and Earth's orbit
We know that the changing position of the Sun in the sky is down to various factors involving the movement and position of our own planet over the year.
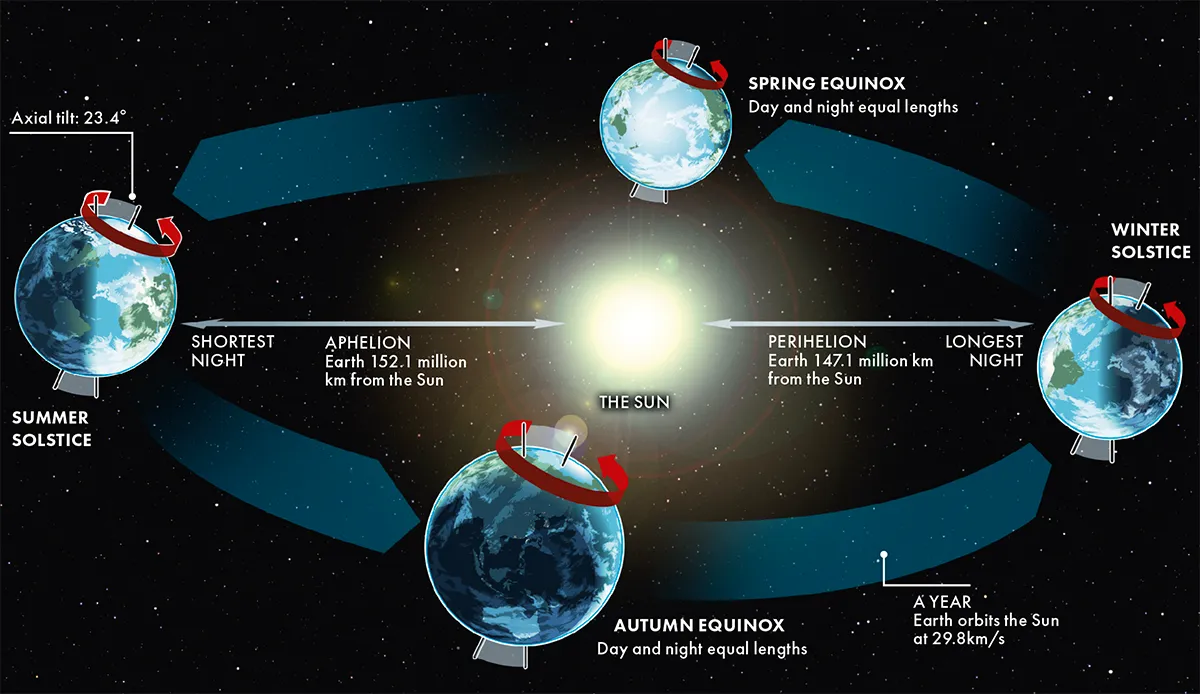
Earth is 150 million kilometres from the Sun and orbits it along a slightly elliptical path at a speed of 107,208 kilometres per hour.
One orbit takes approximately 365 days.
Our planet isn’t upright in its orbit; it’s tilted at an angle of 23.4° and spins on an axis (an imaginary line that passes through the North Pole to the South Pole) at a speed of 1,670 kilometres per hour.
One spin takes 24 hours.

The tilt, rotation and elliptical orbit of Earth all give rise to changes in the amount of sunlight that we receive in each hemisphere throughout the year, and this is why we have seasons.
When the top of Earth is tilted towards the Sun, the Northern Hemisphere experiences summer, while the Southern Hemisphere faces away and people there have their winter.
Six months later and the seasons flip in each hemisphere.
Our seasons in the astronomical calendar are determined by two solstices and two equinoxes a year.
A solstice occurs at the two points in Earth’s orbit when our globe is at its maximum tilt either towards or away from the Sun.
Equinoxes happen at the two points of the orbit when the Sun appears directly over the equator.
The solstices and equinoxes divide the year into four parts: spring, summer, autumn and winter.
Summer solstice and Earth's tilt
The summer solstice occurs when that hemisphere’s pole is tilted at its maximum angle towards the Sun.
During this time, we experience a day with the longest period of daylight, 16 or so hours in the UK.
On the day of summer solstice the Sun reaches the most northerly point along its path through the sky (the ecliptic) before moving south again.
This is what is meant by the Sun ‘standing still’.
The winter solstice is the opposite and occurs in December, when the North Pole is tilted at its maximum angle away from the Sun and the Sun reaches its most southerly point in the sky.
You might think that because Earth is tilted towards the Sun during the summer solstice, that that’s when we are closest to our star.
But this is not the case. In fact, the point at which our planet is closest to the Sun (perihelion) is in early January.
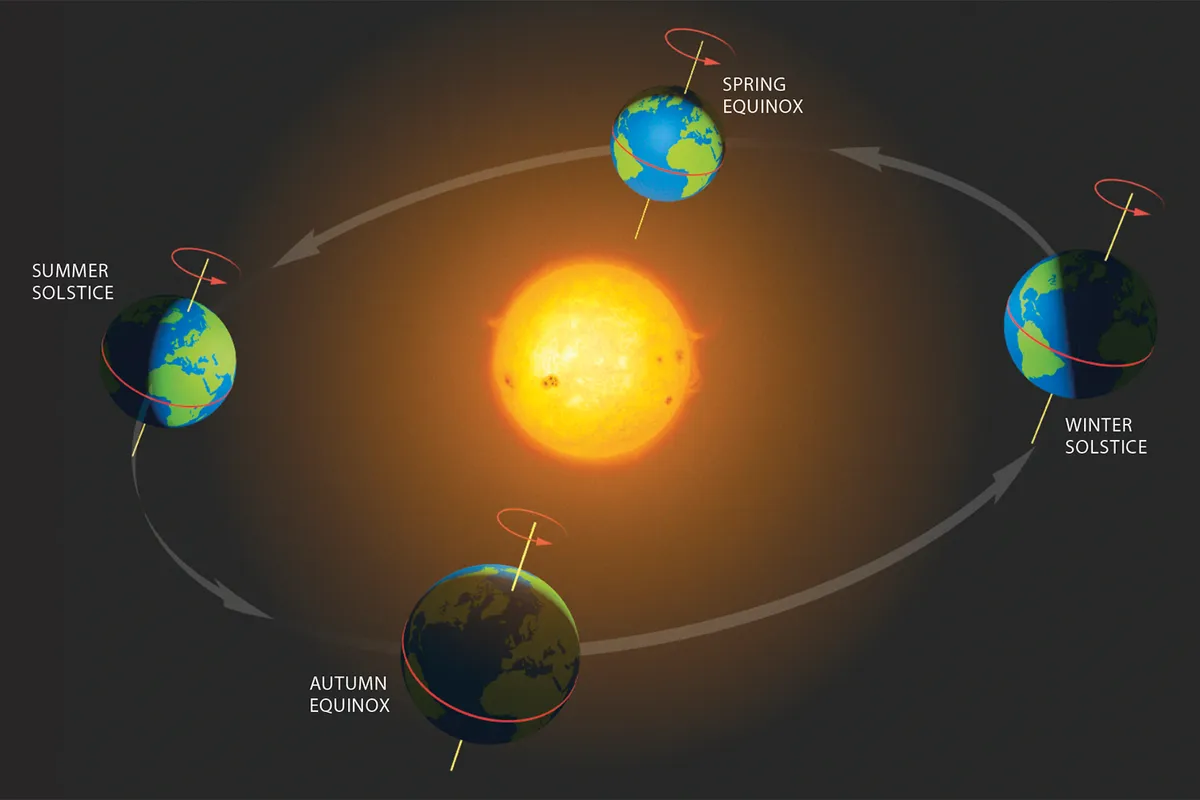
Equinoxes explained
Falling between the summer and winter solstices are the spring and autumn equinoxes.
‘Equinox’ again comes from Latin and translates as ‘equal night’.
The equinoxes happen when Earth’s axis points neither towards nor away from the Sun, a point when the Sun crosses the celestial equator going northwards or southwards depending on the time of year.
The Sun is above the horizon for the same amount of time as it is below it.
This article originally appeared in the June 2023 issue of BBC Sky at Night Magazine.

