It’s the question that always comes up when thinking about the origin of the Universe: what came before the Big Bang?
And if there was no ‘before’, what was the cause of the Big Bang in the first place?
Until a few centuries ago, the answer was easy: some eternal deity set everything in motion.
Even Isaac Newton believed that God created the Universe, some 6,000 years ago.
Later, many scientists, including young Albert Einstein, assumed the Universe itself to be eternal and everlasting.
For more cosmology, read our guides to nuclear pasta, spacetime, supersymmetry and antimatter.
The beginning of the Universe
But when cosmic expansion was discovered, Belgian cosmologist (and Jesuit priest) Georges Lemaître realised there must have been a beginning – a scientific version of Genesis, so to speak.
Not that everyone immediately agreed.
Well into the 1960s, Fred Hoyle’s steady-state theory was quite popular among iconoclastic scientists as well as lay people.
Hoyle accepted the expansion of the Universe, but he didn’t believe in the Big Bang.
Instead, he assumed that a slow, continuous creation of new matter could keep the average density and the general properties of the Universe constant over time.
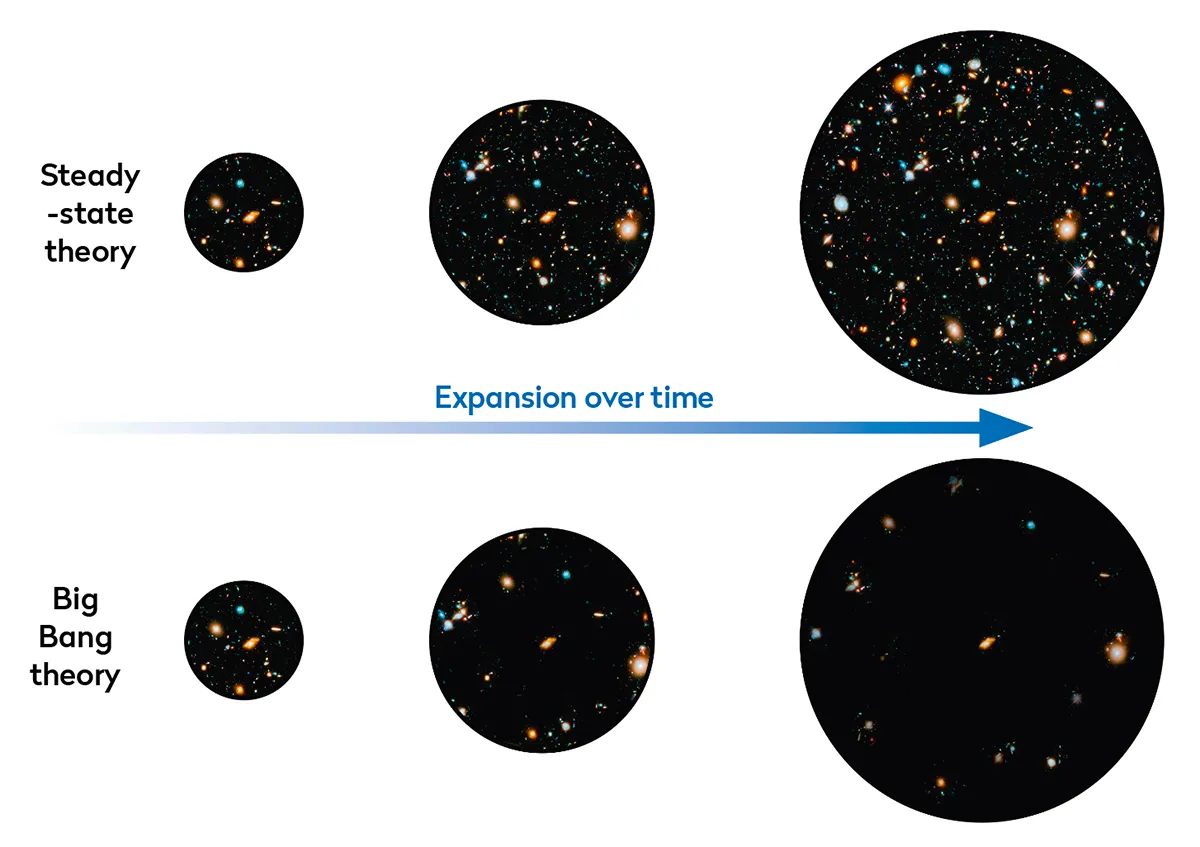
The 1964 discovery of the cosmic microwave background was the major nail in the coffin of the steady-state theory.
Ever since, supporting evidence for the Big Bang origin of our Universe has accumulated to a point where there’s hardly any doubt left.
Still, no one has the final answer to the question "what happened before the Big Bang?".
Could there have been a Universe before the Big Bang?
Most scientists simply ignore the question, as it seems to be too hard a nut to crack.
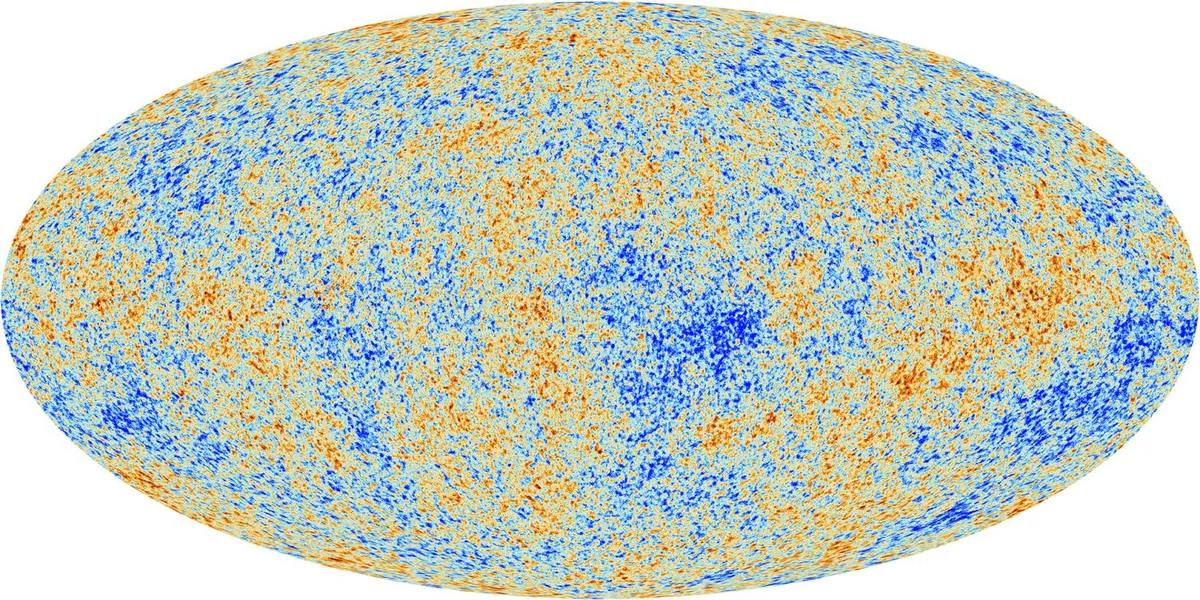
Beginning of time
When astronomers talk about the Big Bang, they usually do not refer to the very beginning of the Universe (time zero), but to the incredibly hot and compact state of the Universe in the first couple of minutes of its existence.
To some extent, this is because no one has a real clue about the true nature of time, let alone about the beginning of time.
British physicist Julian Barbour, for one, has argued that time doesn’t even exist, except as an illusion in our minds.
According to others (including Stephen Hawking), time came into existence together with the Universe, rendering the whole concept of the word ‘before’ meaningless.
Asking what happened before the Big Bang would be like asking what lies north of the North Pole, or what distance is shorter than zero.

Alternative theories
Then again, we simply don’t know whether or not there was time before the Big Bang.
According to the once-popular idea of the cyclic (or oscillatory) Universe, the current expansion of space could one day revert into a contraction, and the resulting Big Crunch could bounce into a new Big Bang, starting the next cycle of an eternal sequence.
For more on this, read our interview with Katie Mack about the end of the Universe.
It’s just one of many hypotheses in which our Universe is not unique, but part of a possibly infinite multiverse, one way or another.
And if the multiverse is also infinite in time, we’re back to the idea that everything has existed forever, conveniently circumnavigating the nagging question of a beginning.

Finally, South African physicist Neil Turok thinks the Big Bang not only spawned our Universe, but also an anti-Universe, composed of antimatter and running backward in time.
Again, an intriguing idea, but there’s also no chance of confirmation (or rejection!) via observations.
In the end, we have to admit we’re ignorant about the true beginning of the Universe.
And even if we lean towards an eternal multiverse with no real beginning at all, we don’t know why there is something (or, more to the point, why there is everything) instead of nothing.
This article originally appeared in the June 2023 issue of BBC Sky at Night Magazine.

